|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CHFClCF2-O-CF2H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chlorine |
|
|
|
Nuclear
Quadrupole Coupling Constants |
|
|
in
2-Chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl-difluoromethyl ether
|
|
|
|
|
(aka
Enflurane)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Complete nqcc tensors for both 35Cl
and 37Cl
in each of three structural conformers of
2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl-difluoromethyl ether (Enflurane) have
been calculated on PBE1PBE/6-311+G(3d,3p) optimized molecular
structures. (This particular optimization was chosen based on its
success for calculation of Cl nqcc tensors in 2-chloroethyl
ethyl sulfide.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
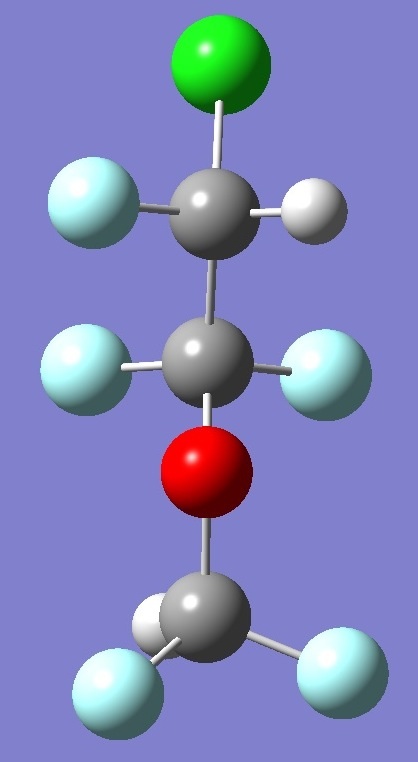
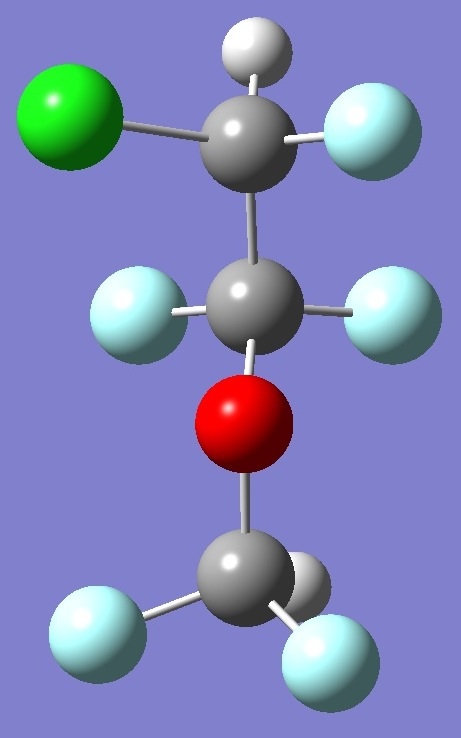
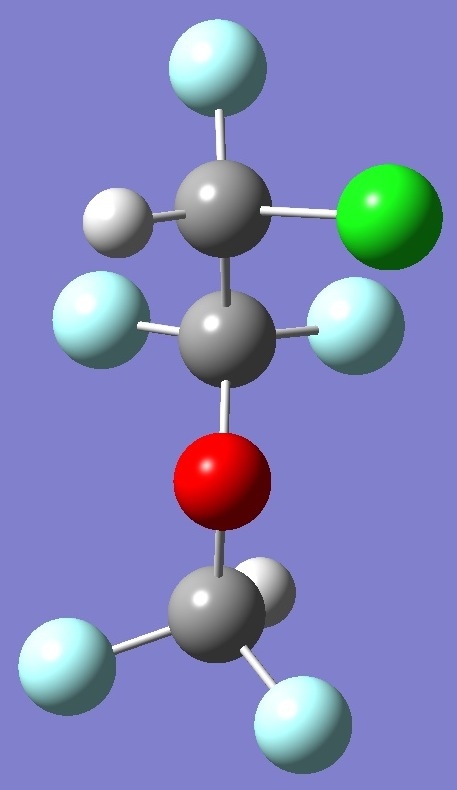
The conformers of enflurane
considered here are shown below:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enflurane T
|
|
Enflurane G+
|
|
Enflurane G-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calculated nqcc tensors for Enflurane
I are given below in Tables 1 and 2. Structure parameters are
given in Table 3, rotational constants and dipole moments in Table 4.
(For G+ and G-, click on the above figure headings.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Tables 1 and 2, subscripts a,b,c
refer to the
principal axes of the inertia tensor; x,y,z to the principal axes
of the nqcc tensor. ETA = (Xxx - Xyy)/Xzz.
Ø (degrees) is the angle between the principal z-axis of the
nqcc tensor and the CCl bond axis.
|
|
|
RMS is the root mean square difference between calculated and
experimental diagonal nqcc's (percentage of the average of the
magnitudes of the experimental nqcc's). RSD is the calibration
residual standard deviation of the B1LYP/TZV(3df,2p) model for calculation of the chlorine efg's/nqcc's. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1.
35Cl
nqcc's in Enflurane, T (MHz). Calculation was made
on the PBE1PBE/6-311+G(3d,3p) optimized structure. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Calc |
|
Expt [1]
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35Cl |
Xaa |
- |
48.42 |
-
|
46.9715(36)
|
|
| |
|
Xbb |
|
18.60 |
|
18.4503(50)
|
|
|
|
Xcc |
|
29.82 |
|
28.5211(86)
|
|
|
|
Xab |
- |
38.16 |
|
37.61(16) *
|
|
|
|
Xac |
|
30.16 |
|
31.36(20) *
|
|
|
|
Xbc |
|
13.20 |
|
13.74228) *
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS
|
|
1.12 (3.6 %)
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSD
|
|
0.49 (1.1 %)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
35.84 |
|
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
|
40.10 |
|
|
|
| |
|
Xzz |
- |
75.94 |
|
|
|
|
|
ETA |
|
0.056 |
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,CCl |
|
1.52
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Absolute value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2.
37Cl
nqcc's in Enflurane, T (MHz). Calculation was made
on the PBE1PBE/6-311+G(3d,3p) optimized structure. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Calc |
|
Expt [1]
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37Cl |
Xaa |
- |
38.33 |
-
|
37.1858(47)
|
|
| |
|
Xbb |
|
14.86 |
|
14.7407(63)
|
|
|
|
Xcc |
|
23.46 |
|
22.4451(110)
|
|
|
|
Xab |
- |
29.88 |
|
29.33(15) *
|
|
|
|
Xac |
|
23.85 |
|
24.91(17) *
|
|
|
|
Xbc |
|
10.34 |
|
10.61(14) *
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS
|
|
0.88 (3.6 %)
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSD
|
|
0.44 (1.1 %)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
28.24 |
|
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
|
31.60 |
|
|
|
| |
|
Xzz |
- |
59.85 |
|
|
|
|
|
ETA |
|
0.056 |
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,CCl |
|
1.52
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Absolute value. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
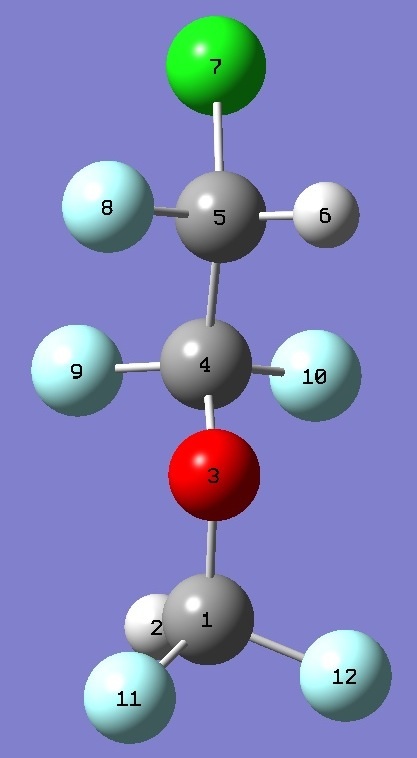
| Table 3. Enflurane, T.
Selected structure parameters (Å and
degrees). Complete structure is given here in Z-matrix format. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
C(1)O |
1.3849 |
|
|
OC(4) |
1.3624 |
|
|
C(4)C(5) |
1.5336 |
|
|
C(5)Cl |
1.7549 |
|
|
C(1)OC(4) |
116.90 |
|
|
OC(4)C(5) |
107.20 |
|
|
C(4)C(5)Cl |
110.87 |
|
|
OC(4)C(5)Cl |
178.43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Table 4. 35Cl-Enflurane, T. Rotational constants (MHz) and dipole moments (D). |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
Calc |
Expt [1]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
2390.4 |
2383.59171(19)
|
|
|
B |
632.6 |
631.455371(79)
|
|
|
C |
575.0 |
574.955289(88)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|µa| |
0.30 |
|
|
|
|µb| |
0.79 |
|
|
|
|µc| |
0.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1] C.Pérez, E.Caballero-Mancebo, A.Lesarri, E.J.Cocinero, I.Alkorta,
R.D.Suenram, J.-U.Grabow, and B.H.Pate, Chem.Euro.J. 22(28),9804(2016). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enflurane
G+
|
2-Chloroethyl
ethyl sulfide |
Chloromethyl
methyl ether |
|
|
Enflurane G-
|
Chloromethyl
Ethyl Ether |
Isoflurane
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table of Contents |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecules/Chlorine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enflurane_I.html |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last
Modified 8 June 2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



