|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NH2CH2C(=O)OH
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nitrogen |
|
|
|
Nuclear
Quadrupole Coupling Constants |
|
|
in Glycine
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calculation
of the
nitrogen nqcc's in glycine was made here on the molecular
structures given by HF/6-311+G(d,p) and HF/6-311++G(3df,3pd)
optimizations. These are compared with the experimental nqcc's [1] in Tables 1 and 2. Structure
parameters are
given in Table 3, rotational constants in Table 4.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
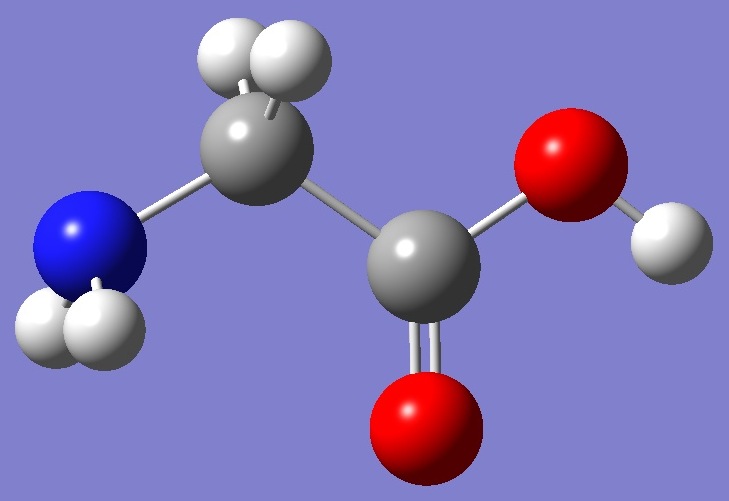
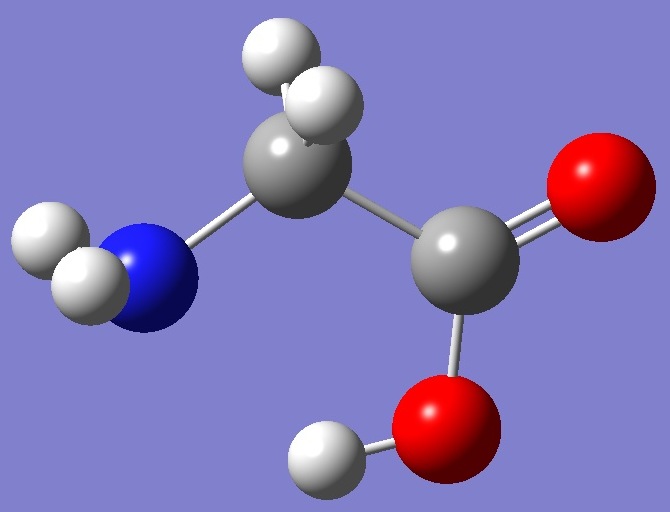
Calculation was made on each of the two lowest energy conformers shown below: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conformer I |
|
Conformer II |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Tables 1 and 2, subscripts a,b,c refer to the
principal axes of the inertia tensor; x,y,z to the principal axes
of the nqcc tensor.
Ø (degrees) is the angle between its subscripted
parameters. ETA = (Xxx - Xyy)/Xzz. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSD is the
calibration residual standard deviation of the B3PW91/6-311+G(df,pd) model for calculation of nitrogen nqcc's. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1. 14N nqcc's in Glycine I (MHz). Calculation was made
on (1) HF/6-311+G(d,p) and (2) HF/6-311++G(3df,3pd) optimized structures. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. (1)
|
|
Calc. (2) |
|
Expt. [1] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xaa |
- |
1.308 |
- |
1.330 |
- |
1.208(9) |
|
|
Xbb |
- |
0.592 |
- |
0.561 |
- |
0.343(8) |
|
|
Xcc |
|
1.900 |
|
1.891 |
|
1.552(10) |
|
|
|Xab| |
|
4.021 |
|
4.005 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
0.254 (24 %) |
|
0.243 (24 %) |
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
0.030 (1.3 %) |
0.030 (1.3 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
3.087 |
|
3.078 |
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
|
1.900 |
|
1.891 |
|
|
|
|
Xzz |
- |
4.987 |
- |
4.969 |
|
|
|
|
ETA |
- |
0.238 |
- |
0.239 |
|
|
|
|
Øz,a |
|
42.45 |
|
42.26 |
|
|
|
|
Øa,NC |
|
31.60 |
|
31.67 |
|
|
|
|
Øz,NC * |
|
105.94 |
|
106.07 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Here and in Table 2, this is the angle between the external (to the H2NC pyrimid and in the ab-plane) z-axis and the NC axis. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2. 14N nqcc's in Glycine II (MHz). Calculation was made
on (1) HF/6-311+G(d,p) and (2) HF/6-311++G(3df,3pd) optimized structures. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. (1)
|
|
Calc. (2) |
|
Expt. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xaa |
|
1.750 |
|
1.762 |
|
1.773(2) |
|
|
Xbb |
- |
3.575 |
- |
3.584 |
- |
3.194(4) |
|
|
Xcc |
|
1.826 |
|
1.822 |
|
1.421(4) |
|
|
|Xab| |
|
2.645 |
|
2.629 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
0.321 (15 %) |
|
0.323 (15 %) |
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
0.030 (1.3 %) |
0.030 (1.3 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
2.840 |
|
2.839 |
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
|
1.826 |
|
1.822 |
|
|
|
|
Xzz |
- |
4.666 |
- |
4.661 |
|
|
|
|
ETA |
- |
0.217 |
- |
0.218 |
|
|
|
|
Øz,a |
|
67.59 |
|
67.74 |
|
|
|
|
Øa,NC |
|
37.69 |
|
37.61 |
|
|
|
|
Øz,NC |
|
105.28 |
|
105.34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| Table 3. Glycine. Selected molecular structure parameters (Å
and degrees). Complete structures are given here in Z-matrix format: Glycine I and Glycine II. |
| |
|
|
|
|
ropt (1) = HF/6-311+G(d,p) optimization. |
|
ropt (2) = HF/6-311++G(3df,3pd) optimization. |
| |
|
|
|
| Conformer I |
|
ropt (1) |
ropt (2) |
| |
|
|
|

|
CC |
1.5154 |
1.5142 |
| CN |
1.4364 |
1.4352 |
| NH |
0.9997 |
0.9978 |
| CCN |
115.53 |
115.49 |
| CNH |
111.18 |
111.10 |
| CCNH |
±59.51 |
±59.36 |
|
|
|
|
| Conformer II |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
CC |
1.5270 |
1.5252 |
| CN |
1.4550 |
1.4527 |
| NH |
0.9975 |
0.9953 |
| CCN |
112.80 |
113.06 |
| CNH |
112.78 |
112.74 |
| CCNH |
±118.42 |
±118.43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Table 4. Glycine. Rotational Constants (MHz). Normal Species. |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
ropt (1) = HF/6-311+G(d,p) optimization. |
|
ropt (2) = HF/6-311++G(3df,3pd) optimization. |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. ropt (1) |
Calc. ropt (2) |
Expt. [1] |
|
|
|
|
|
| I |
A |
10681.0 |
10727.8 |
10341.5279(49) |
|
B |
3919.1 |
3930.9 |
3876.1806(23) |
|
C |
2961.7 |
2971.6 |
2912.3518(16) |
| |
|
|
|
|
| II |
A |
10334.4 |
10375.0 |
10130.1521(57) |
|
B |
4103.2 |
4105.9 |
4071.5120(17) |
|
C |
3037.4 |
3041.9 |
3007.4852(14) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1] F.J.Lovas, Y.Kawashima, J.-U.Grabow, R.D.Suenram, G.T.Fraser, and E.Hirota, Astrophys. 455,L201(1995).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related ... |
|
|
V.V.Ilyushin, E.A.Alekseev, S.F.Dyubko, R.A.Motiyenko, and F.J.Lovas, J.Mol.Spectrosc. 231,15(2005). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N-Acetylglycine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table of Contents |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecules/Nitrogen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Glycine.html |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last
Modified 23 Feb 2006 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



