|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CH2=CH-O-C(=O)Cl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chlorine |
|
|
|
Nuclear
Quadrupole Coupling Constants |
|
|
in
Vinyl Chloroformate
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chlorine nuclear quadrupole coupling
constants in vinyl chloroformate were
determined by Bimler et al., as well as a heavy atom substitution
structure [1]. |
|
|
Calculation of the nqcc's was made
here on this substitution structure (with CH geometries given by
MP2/6-31G(d,p) partial optimization), and on a molecular
structure given by MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ optimization. These are
compared with the experimental nqcc's [1] in Tables 1 and 2.
Structure parameters are
given in Table 3, rotational constants in Table 4.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Tables 1 and 2, subscripts a,b,c
refer to the
principal axes of the inertia tensor; subscripts x,y,z to the principal
axes
of the nqcc tensor.
Ø (degrees) is the angle between its subscripted
parameters. ETA = (Xxx - Xyy)/Xzz. |
|
|
RMS is the root mean square
difference between calculated and experimental diagonal nqcc's
(percentage of the average of the magnitudes of the experimental
nqcc's). RSD is the calibration residual standard deviation of
the B1LYP/TZV(3df,3p) model for calculation of the nqcc's. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1. 35Cl nqcc's in Vinyl
Chloroformate (MHz). Calculation was made on the (1) substitution
and (2) MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ structures. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. (1)
|
|
Calc. (2) |
|
Expt. [1] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xaa |
-
|
38.68
|
-
|
37.00
|
-
|
37.811(7)
|
|
|
Xbb |
|
11.73
|
|
9.97
|
|
9.965(8)
|
|
|
Xcc |
|
26.95
|
|
27.03
|
|
27.846(11)
|
|
|
|Xab| |
-
|
51.26
|
-
|
52.73
|
-
|
51.79(26)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
1.25 (5.0 %)
|
0.66 (2.6 %)
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
0.49 (1.1 %)
|
0.49 (1.1 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
43.65
|
|
44.21
|
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
|
26.95
|
|
27.03
|
|
|
|
|
Xzz |
-
|
70.60
|
-
|
71.24
|
|
|
|
|
ETA |
-
|
0.236
|
-
|
0.241
|
|
|
|
|
Øa,z |
|
31.91
|
|
33.00
|
|
|
|
|
Øa,CCl |
|
32.86
|
|
33.59
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,CCl |
|
0.95
|
|
0.59
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2. 37Cl nqcc's in Vinyl
Chloroformate (MHz). Calculation was made on the (1) substitution
and (2) MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ structures. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. (1)
|
|
Calc. (2) |
|
Expt. [1] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xaa |
-
|
31.13
|
-
|
29.82
|
-
|
30.450(15)
|
|
|
Xbb |
|
9.89
|
|
8.52
|
|
8.502(15)
|
|
|
Xcc |
|
21.24
|
|
21.30
|
|
21.948(22)
|
|
|
|Xab| |
-
|
40.08
|
-
|
41.25
|
-
|
40.4(7)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
0.99 (4.8 %)
|
0.52 (2.6 %)
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
0.44 (1.1 %)
|
0.44 (1.1 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
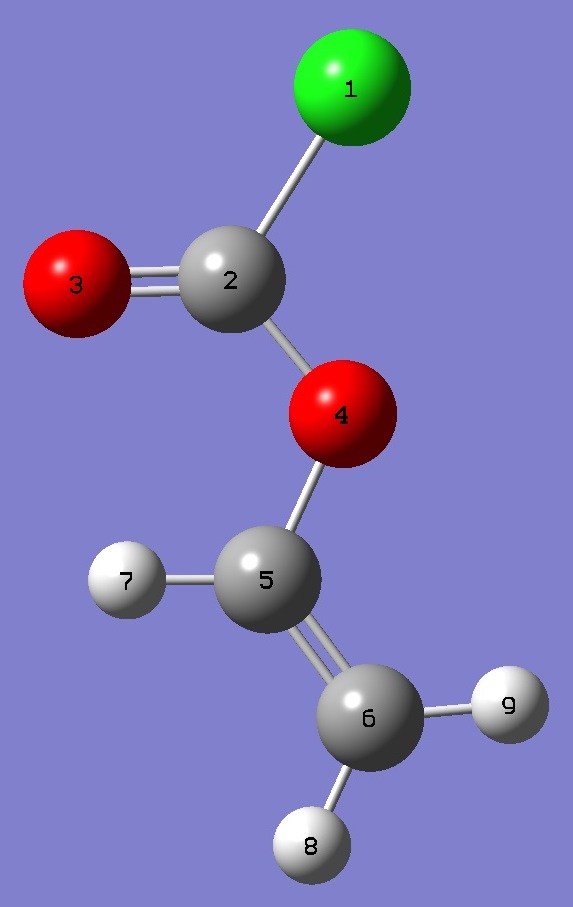
| Table 3. Vinyl Chloroformate.
Heavy atom structure parameters (Å and
degrees). |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
rs = substitution
structure, with CH geometries given by MP2/6-31G(d,p) partial
optimization |
|
ropt =
MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ optimization
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rs |
|
ropt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ClC(2) |
|
1.754
|
|
1.7422
|
| C(2)O(3) |
|
1.196
|
|
1.1949
|
| C(2)O(4) |
|
1.312
|
|
1.3422
|
| O(4)C(5) |
|
1.402
|
|
1.3958
|
| C(5)C(6) |
|
1.330
|
|
1.3264
|
| ClC(2)O(3) |
|
122.0
|
|
123.98
|
| ClC(2)O(4) |
|
108.6
|
|
108.08
|
| O(3)C(2)O(4) |
|
129.3
|
|
127.94
|
| C(2)O(4)C(5) |
|
115.7
|
|
115.76
|
| O(4)C(5)C(6) |
|
118.6
|
|
118.72 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Table 4. Vinyl
Chloroformate. Rotational Constants (MHz). 35Cl Species. |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
rs
= substitution structure, with CH geometries given by
MP2/6-31G(d,p) partial optimization |
|
ropt =
MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ optimization |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc rs |
Calc ropt |
Expt. [1] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
7773.1
|
7698.3
|
7746.511(4)
|
|
B |
1630.2
|
1630.4
|
1626.5050(11)
|
|
C |
1347.6
|
1345.5
|
1345.0950(10)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1] J.Bimler, S.Broadbent, K.A.Utzat,
R.K.Bohn, A.Restrepo, H.H.Michels, N.S.True, J.Mol.Struct.
1023,87(2012).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table of Contents |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecules/Chlorine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CH2CHOCOCl.html |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last
Modified 12 Oct 2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

