|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
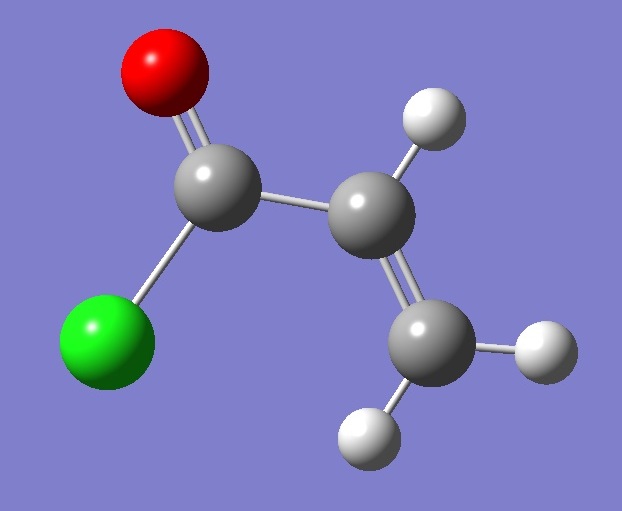
s-t-CH2CHCOCl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chlorine |
|
|
|
Nuclear
Quadrupole Coupling Constants |
|
|
|
in
s-trans-Acryloyl Chloride |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calculation of the chlorine nqcc's in
s-trans-acryloyl chloride was made on a molecular structure derived ab
initio (see below). These are compared with the
experimental nqcc's of Onda et al. [1] in Table 1. Structure
parameters are given in Table 2, atomic coordinates in Table 3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Table 1, RMS is the root mean
square difference between calculated and experimental diagonal nqcc's
(percentage of the average of the magnitudes of the experimental
nqcc's). RSD is the calibration residual standard deviation for
the B1LYP/TZV(3df,2p) model for calculation of the chlorine
nqcc's. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subscripts a,b,c refer to the
principal axes of the inertia tensor; x,y,z to the principal axes
of the nqcc tensor. The nqcc y-axis is chosen coincident with the
inertia c-axis, these are perpendicular to the molecular plane.
Ø (degrees) is the angle between its subscripted
parameters. ETA = (Xxx - Xyy)/Xzz. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1. Chlorine
nqcc's in s-trans-Acryloyl Chloride (MHz). |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. |
|
Expt. [1] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35Cl |
Xaa |
|
1.41 |
|
0.6757(29) |
|
|
|
Xbb |
- |
24.86 |
- |
24.4537(25) |
|
|
|
Xcc |
|
23.45 |
|
23.781(5) |
|
|
|
|Xab| |
|
48.51 |
|
47.55(31) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
0.52 (3.2 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
0.49 (1.1 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
38.53 |
|
33.307(9) |
|
|
|
Xyy |
|
23.45 |
|
23.781(5) |
|
|
|
Xzz |
- |
61.98 |
- |
57.088(9) |
|
|
|
ETA |
- |
0.243 |
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,a |
|
52.57 |
|
52.59 |
|
|
|
Øa,CCl |
|
54.52 |
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,CCl |
|
1.95 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37Cl |
Xaa |
|
- 2.11 |
|
|
|
|
|
Xbb |
- |
16.37 |
|
|
|
|
|
Xcc |
|
18.48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|Xab| |
|
38.96 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Structure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The molecular
structure was optimized at the MP2/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory
assuming Cs symmetry. The optimized CC bond
lengths, single and double, were corrected using equations
obtained from linear regression analysis of the data given in Table
IX of Ref. [2]. For C=O, the bond length was corrected using the
equation
derived from the data in Table 2 of Ref. [3]. For the CCl bond,
the structure was optimized at the MP2/6-311+G(2d,p) level and
corrected by linear regression analysis of the data given in Table 4 of
Ref. [4].
The CH bond lengths were corrected using r = 1.001 ropt,
where ropt is obtained by MP2/6-31G(d,p) optimization [5].
Interatomic angles used in the calculation are those given by
MP2/6-311+G(d,p) optimization. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Table 2. Structure
parameters (Å and degrees). Structure is
given here in Z-matrix format. |
|
|
|
 |
C(3)Cl |
1.792 |
| C(3)=O |
1.191 |
| C(2)-C(3) |
1.3335 |
| C(1)=C(2) |
1.474 |
| C(2)H |
1.083 |
| C(1)Hc |
1.080 |
| C(1)H |
1.081 |
| C(2)C(3)Cl |
115.28 |
|
C(2)C(3)O |
124.77 |
|
CCC |
125.49 |
|
C(3)C(2)H |
113.03 |
|
C(2)C(1)Hc |
121.66 |
|
C(2)C(1)H |
120.03 |
|
|
|
|
Hc is cis with
Cl. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Table 3. Atomic coordinates ropt |
| (More figures are shown than
are significant.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a (Å) |
|
b (Å) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cl |
- |
1.084356 |
- |
0.817606 |
|
O |
- |
0.539592 |
|
1.724838 |
|
C |
|
1.406400 |
|
0.380750 |
|
C |
- |
0.044316 |
|
0.641703 |
|
C |
|
1.976130 |
- |
0.824916 |
|
H |
|
1.999842 |
|
1.286684 |
|
H |
|
3.053437 |
- |
0.914192 |
|
H |
|
1.387174 |
- |
1.730195 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1] M.Onda, K.Kuratomi, M.Mori,
H.Miyazaki, I.Yamaguchi, and Y.Niide, J.Mol.Spectrosc. 171,565(1995). |
|
|
[2] J.Demaison, J.Cosléou,
R.Bocquet, and A.G.Lesarri, J.Mol.Spectrosc. 167,400(1994). |
|
|
[3] J.Demaison, G.Wlodarczak,
H.Rück, K.H.Wiedenmann, and H.D.Rudolph, J.Mol.Struct.
376,399(1996). |
|
|
[4] I.Merke, L.Poteau, G.Wlodarczak,
A.Bouddou, and J.Demaison, J.Mol.Spectrosc. 177,232(1996). |
|
|
[5] J.Demaison and G.Wlodarczak,
Structural Chem. 5,57(1994). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R.Kewley, D.C.Hemphill, and R.F.Curl
Jr., J.Mol.Spectrosc. 44,443(1972): For 35Cl, (Xaa,
Xbb, Xcc) = (0.6, -24.4, 23.8 MHz); and for 37Cl,
(0.3, -17.2, 16.9 MHz). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HCOCl |
FCOCl |
CH3COCl |
|
|
|
OCCl2 |
SCCl2 |
SCFCl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table of Contents |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecules/Chlorine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
stCH2CHCOCl.html |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last
Modified 13 May 08 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

