|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
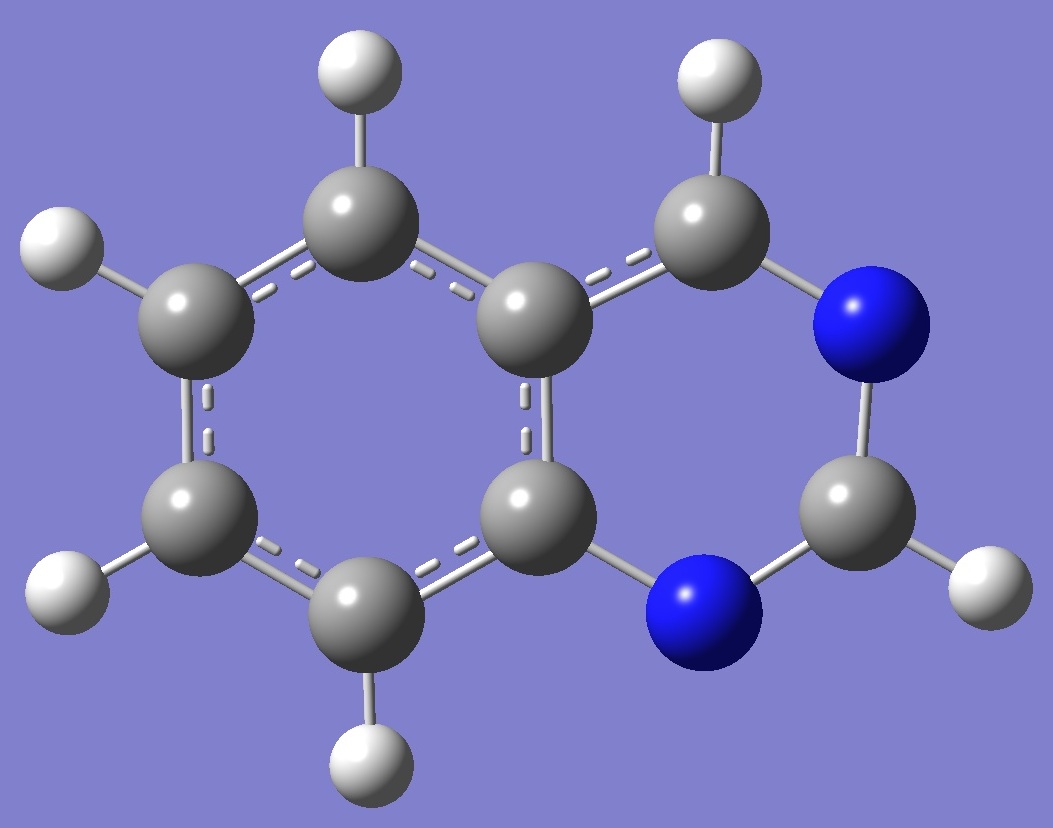
Quinazoline
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nitrogen
|
|
|
Nuclear
Quadrupole Coupling Constants |
|
|
|
in
Quinazoline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nitrogen nqcc tensors in quinazoline
were calculated on a molecular structure optimized at the
B3P86/6-31G(3d,3p) level of theory (ropt). These
calculated nqcc's are compared with the experimental values of
McNaughton et al. [1] in Tables 1 and 2. Structure
parameters are
given in Table 3, rotational constants and electric dipole moments in
Table 4. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Tables 1 and 2, subscripts a,b,c
refer to
principal axes of the inertia tensor, subscripts x,y,z to principal
axes of the nqcc tensor. The nqcc y-axis is chosen coincident
with the inertia c-axis, these are perpendicular to the plane of the
molecule. Ø (degrees) is the angle between its subscripted
parameters. ETA = (Xxx - Xyy)/Xzz. |
|
|
RMS is the root mean square
difference between calculated and experimental nqcc's (percentage of
average experimental nqcc). RSD is the residual stand deviation
of calibration of the B3PW91/6-311+G(df,pd) model for calculation of
the nqcc's (which may be taken as the uncertainty in calculated nqcc's,
notwithstanding uncertainties in the calculated molecular structure). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1. 14N(15)
nqcc's in Quinazoline (MHz). Calculation was made
on the B3P86/6-31G(3d,3p) ropt structure. This is N(1)
in Ref. [1]. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. |
|
Expt. [1] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14N(15) |
Xaa |
|
1.462 |
|
1.4547(35) |
|
|
|
Xbb |
- |
4.533 |
- |
4.5186 * |
|
|
|
Xcc |
|
3.071 |
|
3.0639 * |
|
|
|
Xab |
- |
0.219 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
0.010 (0.34 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
0.030 (1.3 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
1.470 |
|
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
|
3.071 |
|
|
|
|
|
Xzz |
- |
4.541 |
|
|
|
|
|
ETA |
|
0.353 |
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,b |
|
2.09 |
|
|
|
|
|
Øb,bi |
|
1.39
|
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,bi** |
|
3.48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Calculated here from experimental Xaa and
Xbb - Xcc = -7.5826(75) MHz. |
|
|
** The z-axis makes an angle of
3.48o
with the external bisector ('bi') of the CNC angle and tilts toward
C(4). See Table 3 for atomic numbering. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2. 14N(16)
nqcc's in Quinazoline (MHz). Calculation was made
on the B3P86/6-31G(3d,3p) ropt structure. This is N(2)
in Ref. [1]. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. |
|
Expt. [1] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14N(16) |
Xaa |
- |
3.561 |
- |
3.59205(179) |
|
|
|
Xbb |
- |
0.321 |
- |
0.3503 * |
|
|
|
Xcc |
|
3.241 |
|
3.2417 * |
|
|
|
Xab |
- |
2.368 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
0.025 (1.0 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
0.030 (1.3 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
1.442 |
|
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
|
3.241 |
|
|
|
|
|
Xzz |
- |
4.682 |
|
|
|
|
|
ETA |
|
0.384 |
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,a |
|
25.33 |
|
|
|
|
|
Øa,bi |
|
27.41
|
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,bi** |
|
2.08
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Calculated here from experimental Xaa and
Xbb - Xcc = -2.8914(62) MHz. |
|
|
** The z-axis makes an angle of
2.08o
with the external bisector ('bi') of the CNC angle and tilts toward
C(13). See Table 3 for atomic numbering. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
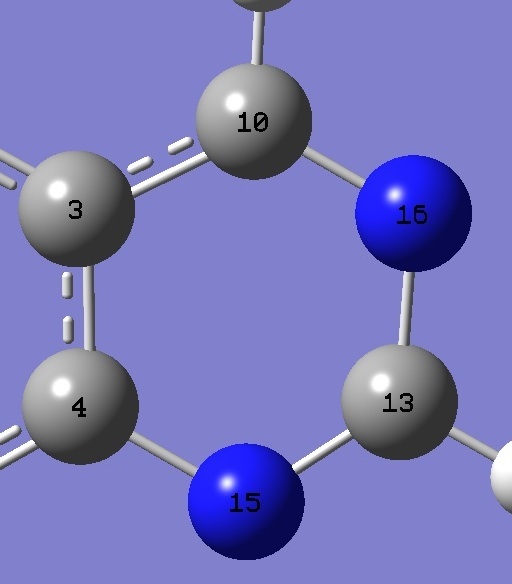
| Table 3. Quinazoline and
Pyrimidine. Selected molecular structure parameters,
B3P86/6-31G(3d,3p) ropt (Å and degrees).
The complete structure of quinazoline is given here in Z-matrix format. |
| |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
Quinazoline |
Pyrimidine |
|
|
|
|
|
C(4)N(15) |
1.3599 |
1.3328 |
|
N(15)C(13) |
1.3093 |
1.3320 |
|
C(13)N(16) |
1.3580 |
1.3320 |
|
N(16)C(10) |
1.3116 |
1.3328 |
|
C(4)N(15)C(13) |
116.38 |
115.70 |
|
N(15)C(13)N(16) |
127.89 |
127.38 |
|
C(13)N(16)C(10) |
115.81 |
115.70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| Table 4.
Quinazoline, ropt.
Rotational constants (MHz) and B3PW91/6-311+G(df,pd) calculated
dipole moments (D). |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc. |
|
Expt. [1] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
3253.20 |
|
3229.85422(55) |
|
B |
|
1283.94 |
|
1276.2106327(191) |
|
C |
|
920.60 |
|
914.9869715(217) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|µa| |
|
2.85 |
|
|
|
|µb| |
|
1.24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1] D.McNaughton, P.D.Godfrey,
M.K.Jahn, D.A.Dewald, and J.-U.Grabow, J.Chem.Phys. 134,154305(2011). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pyrimidine |
Phthalazine |
Quinoxaline |
1,10-Phenanthroline |
|
|
Acridine |
Quinoline |
Isoquinoline |
Phenanthridine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table of Contents |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecules/Nitrogen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quinazoline.html |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last
Modified 20 April 2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

