|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
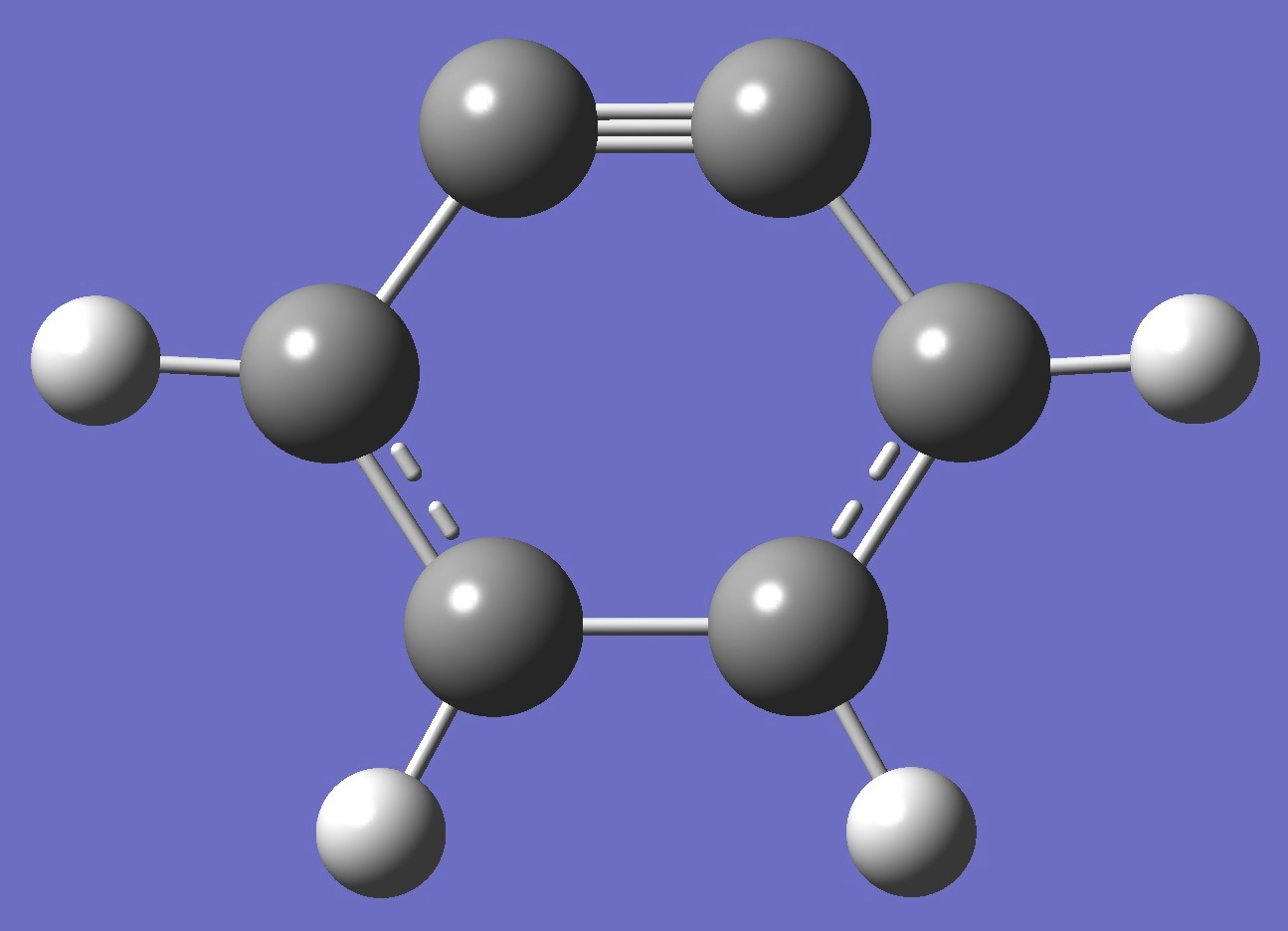
C6H4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deuterium |
|
|
|
Nuclear
Quadrupole Coupling Constants |
|
|
|
in ortho-Benzyne |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deuterium
nqcc's in o-benzyne were measured by Kukolich et al. [1,2], which
authors also determined a substitution molecular structure
[2]. A "pseudo-re" structure was derived by Groner and Kukolich [3].
|
|
|
Calculation of the deuterium nqcc's was
made on these molecular rs and re structures. Calculated
nqcc's are compared with the experimental values [2] in Tables 1 and 2.
Structure parameters are given in Table 3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Tables 1 and 2, subscripts a,b,c refer to the principal axes of the inertia tensor,
the subscripts x,y,z to the principal axes of the nqcc tensor. The
nqcc y-axis is chosen coincident with the inertia c-axis, these are perpendicular
to the plane of the molecule. Ø (degrees) is the angle between
its subscripted parameters. ETA = (Xxx - Xyy)/Xzz. |
|
|
RMS is the root mean square
difference between calculated and experimental nqcc's (percentage
of the average of the magnitudes of the experimental nqcc's). RSD
is the calibration residual standard deviation for the B3LYP/6-31G(df,3p)
model for calculation of the efg's/nqcc's. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1. D(3) nqcc's
in o-Benzyne (kHz). Calculation was
made on rs and re molecular structures.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc /rs |
|
Calc /re |
|
Expt. [2] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xaa |
|
193.6
|
|
193.1 |
|
187.0(21) |
|
|
Xbb |
|
- 91.2
|
|
- 90.7 |
|
- 89.3 *
|
|
|
Xcc |
-
|
102.4
|
- |
102.4 |
|
- 97.7 *
|
|
|
|Xab| |
|
8.3
|
|
7.9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
4.8 (3.8 %)
|
|
4.5 (3.6 %) |
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
1.1 (0.9 %) |
|
1.1 (0.9 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
- 91.5
|
|
- 90.9 |
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
-
|
102.4
|
- |
102.4 |
|
|
|
|
Xzz |
|
193.9
|
|
193.3 |
|
|
|
|
ETA |
|
0.0562
|
|
0.0595 |
|
|
|
|
Øz,a |
|
1.66
|
|
1.59 |
|
|
|
|
Øa,CD |
|
2.35
|
|
1.46
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,CD |
|
0.68
|
|
0.13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Calculated here from experimental Xaa and Xbb - Xcc = 8.4(44) kHz.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2. D(4) nqcc's
in o-Benzyne (kHz). Calculation was
made on rs and re molecular structures.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calc /rs |
|
Calc /re |
|
Expt. [2] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xaa |
|
21.8
|
|
26.6
|
|
20.9(34)
|
|
|
Xbb |
|
80.2
|
|
75.9
|
|
77.9 *
|
|
|
Xcc |
-
|
102.0
|
- |
102.5 |
|
- 98.8 *
|
|
|
|Xab| |
|
137.7
|
|
139.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMS |
|
2.3 (3.5 %)
|
|
4.1 (6.2 %) |
|
|
|
|
RSD |
|
1.1 (0.9 %) |
|
1.1 (0.9 %) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xxx |
|
- 89.8
|
|
- 90.5 |
|
|
|
|
Xyy |
-
|
102.0
|
- |
102.5 |
|
|
|
|
Xzz |
|
191.8
|
|
193.0 |
|
|
|
|
ETA |
|
0.0634
|
|
0.0626 |
|
|
|
|
Øz,a |
|
50.98
|
|
50.01 |
|
|
|
|
Øa,CD |
|
51.05
|
|
50.23
|
|
|
|
|
Øz,CD |
|
0.07
|
|
0.22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Calculated here from experimental Xaa and Xbb - Xcc = 176.7(36) kHz.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| Table 3. o-Benzyne. Molecular structure parameters, rs [2] and re [3] (Å
and degrees). |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
rs |
re |
|
C(1)C(2) |
1.255(8) | 1.255(3)
|
|
C(2)C(3) |
1.40(2) | 1.383(2)
|
|
C(3)C(4) |
1.39(2) | 1.403(2)
|
|
C(4)C(5) |
1.404(14) | 1.405(3)
|
|
C(3)H(3) |
1.08(2) | 1.080(1)
|
|
C(4)H(4) |
1.084(9) | 1.082(1)
|
|
C(1)C(2)C(3) |
126(1) | 126.66(9)
|
|
C(2)C(3)C(4) |
111(1) | 110.98(10)
|
|
C(3)C(4)C(5) |
123(1) | 122.36(8)
|
|
C(2)C(3)H(3) |
123(1) | 127.4(11)
|
|
C(5)C(4)H(4) |
119(1) | 118.73(8)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[1] S.G.Kukolich, C.Tanjaroon, M.C.McCarthy,
and P.Thaddeus, Abstract RC01, 58th Ohio State University Symposium on
Molecular Spectroscopy 2003; J.Chem.Phys. 119,4353(2003). |
|
|
[2] S.G.Kukolich, M.C.McCarthy,
and P.Thaddeus, J.Phys.Chem. A 108,2645(2004).
|
|
|
[3] P.Groner and S.G.Kukolich, J.Mol.Struct. 780-781,178(2006).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Benzene-d1 |
Phenylacetylene-d1 |
Pyridine-4D |
|
Fluorobenzene-d1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table of Contents |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecules/Deuterium |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
o_benzyne.html |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last
Modified 6 Sept 2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
